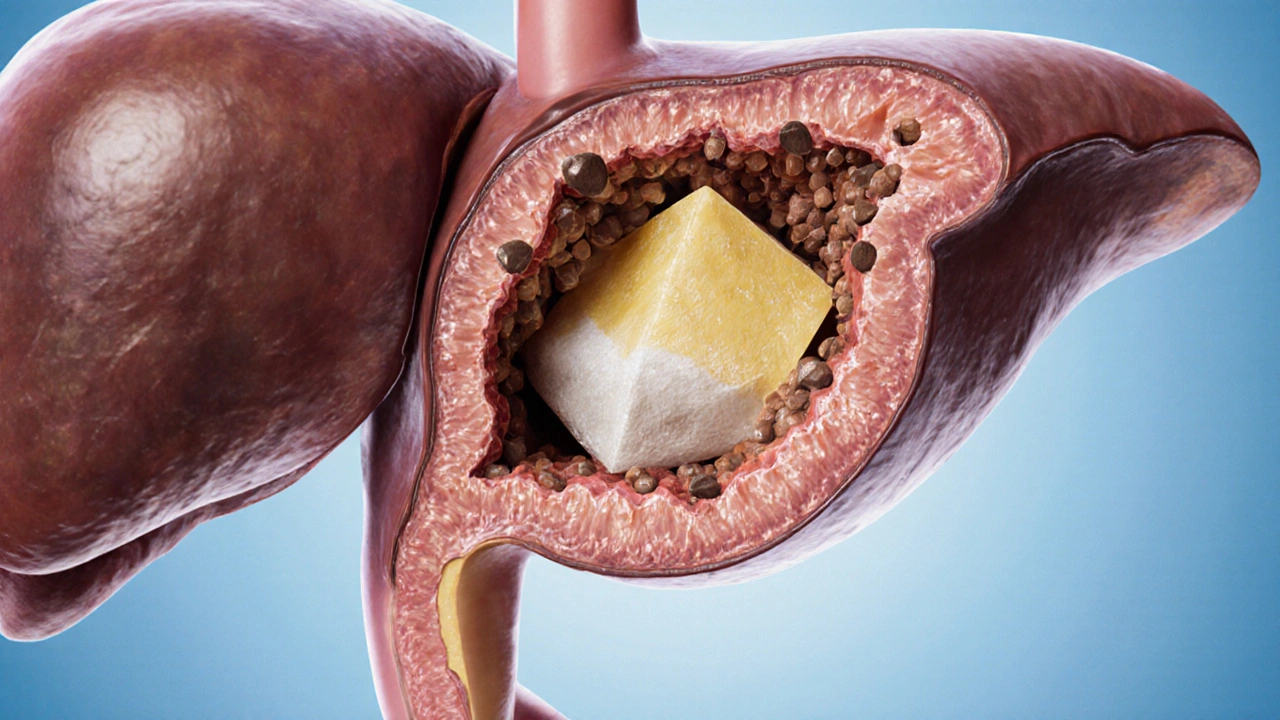
Cholesterol Stones: What They Are and How to Manage Them
When dealing with cholesterol stones, hard deposits formed primarily from cholesterol that lodge in the gallbladder or bile ducts. Also called cholesterol gallstones, they are the most common type of gallstones, a broader group of solid particles that can block bile flow. The formation process hinges on bile, the digestive fluid that emulsifies fats; when bile becomes supersaturated with cholesterol, crystals can nucleate and grow into stones. Understanding this chain – cholesterol excess, bile supersaturation, stone nucleation – helps you see why diet, genetics, and liver function all play a role. In short, cholesterol stones encompass the chemistry of cholesterol, the physiology of bile, and the clinical picture of gallstone disease.
Key Factors That Drive Stone Formation
First, the body’s cholesterol balance matters. High dietary cholesterol or impaired cholesterol metabolism raises the concentration of cholesterol in bile, pushing it past the solubility limit. Second, bile composition is critical; reduced bile salts or phospholipids weaken the fluid’s ability to keep cholesterol dissolved. Third, gallbladder motility influences whether crystals are flushed out or linger long enough to coalesce. Age, obesity, rapid weight loss, and certain medications (like estrogen therapy) also tip the scales. On the flip side, staying hydrated, eating fiber‑rich foods, and maintaining a healthy weight support normal bile flow and can lower the risk of stone buildup. These relationships lead to a clear semantic chain: cholesterol levels affect bile composition, which in turn dictates stone risk.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive deeper into the related health topics we just touched on. Whether you’re curious about how blood‑pressure meds like Irbesartan impact potassium levels, want practical tips on buying affordable generic drugs, or need guidance on managing side effects of inhaled steroids, the collection offers concrete advice you can act on right away. Each piece connects back to the core idea that the body’s chemistry—cholesterol, bile, electrolytes—shapes the health outcomes you experience. Keep scrolling to explore detailed guides, safety checklists, and evidence‑based recommendations that will help you prevent, diagnose, and treat cholesterol stones effectively.
Learn how gallstones affect gallbladder cancer risk, the types of stones, warning signs, diagnostic methods, and steps to lower your chances of developing cancer.
Recent-posts
Dec, 19 2025
Categories
Tags
- online pharmacy
- side effects
- drug interactions
- generic drugs
- online pharmacy UK
- drug safety
- opioid side effects
- pill organizer
- Tadalafil
- arthritis medication
- buy medication online
- prescription medication
- quit smoking
- motion sickness
- Sildenafil
- Vardenafil
- ED medication alternatives
- biologics
- medication safety
- generic medication prices