Variceal Bleeding: Causes, Risks, and How Medications Can Help
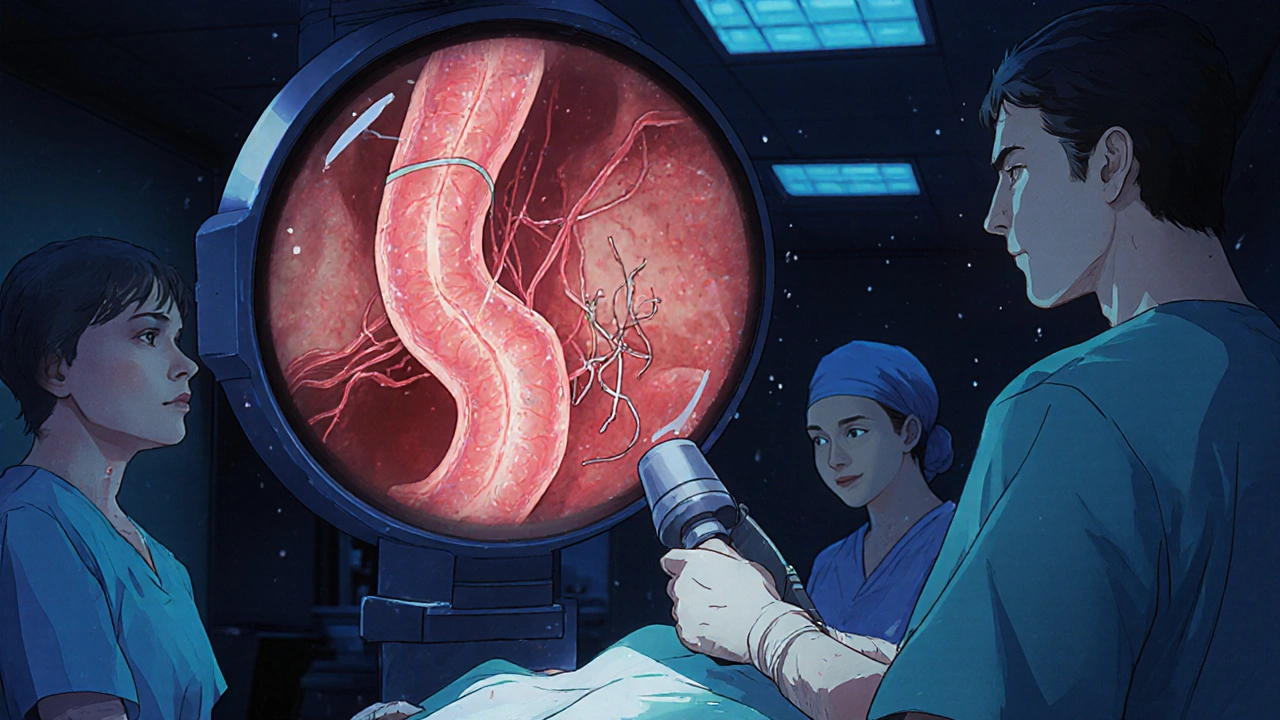
When you have variceal bleeding, a dangerous rupture of swollen veins in the esophagus or stomach caused by high pressure in the liver’s blood vessels. Also known as esophageal varices bleeding, it’s one of the most urgent complications of advanced liver disease. This isn’t just a stomach issue—it’s a sign your liver is struggling to filter blood, forcing fluid to find other paths, and those paths are fragile veins that can burst without warning.
Behind every case of variceal bleeding is portal hypertension, abnormally high pressure in the vein that carries blood from the intestines to the liver. It’s what stretches those veins thin. Common causes include cirrhosis from alcohol, hepatitis, or fatty liver disease. Once a vein ruptures, you lose blood fast—sometimes a liter or more in minutes. Many patients don’t even make it to the hospital without emergency treatment.
That’s where medications come in. beta blockers, like propranolol or nadolol, are the first line of defense. They don’t fix the liver, but they lower pressure in the portal system, reducing the chance of bleeding by up to 50%. For active bleeding, octreotide, a synthetic hormone that tightens blood vessels. is given IV to stop the flow while doctors prepare for endoscopy. These aren’t optional—they’re life-saving. Skipping doses or delaying treatment increases death risk dramatically.
But meds alone aren’t enough. You also need to avoid things that make bleeding worse—like NSAIDs (they thin the blood), alcohol (it worsens liver damage), and high-salt diets (they raise pressure). Some patients need banding or shunt procedures, but medication is the foundation. Even after bleeding stops, long-term beta blocker use cuts the chance of it coming back.
What you’ll find below are real, practical posts that connect directly to this. You’ll see how drugs like beta blockers interact with other prescriptions, why timing matters when taking them, and what to do when a medication runs out. There’s also info on managing side effects, comparing alternatives, and understanding why some treatments work better for certain people. These aren’t theory pieces—they’re tools for patients and caregivers who need to act fast, make smart choices, and avoid mistakes that could cost lives.
Variceal bleeding is a life-threatening complication of liver cirrhosis. Learn how endoscopic banding, beta-blockers like carvedilol, and prevention strategies can stop bleeding and save lives.
Recent-posts
Categories
Tags
- online pharmacy
- side effects
- drug interactions
- generic drugs
- online pharmacy UK
- drug safety
- opioid side effects
- pill organizer
- Tadalafil
- arthritis medication
- buy medication online
- prescription medication
- quit smoking
- motion sickness
- Sildenafil
- Vardenafil
- ED medication alternatives
- biologics
- medication safety
- generic medication prices