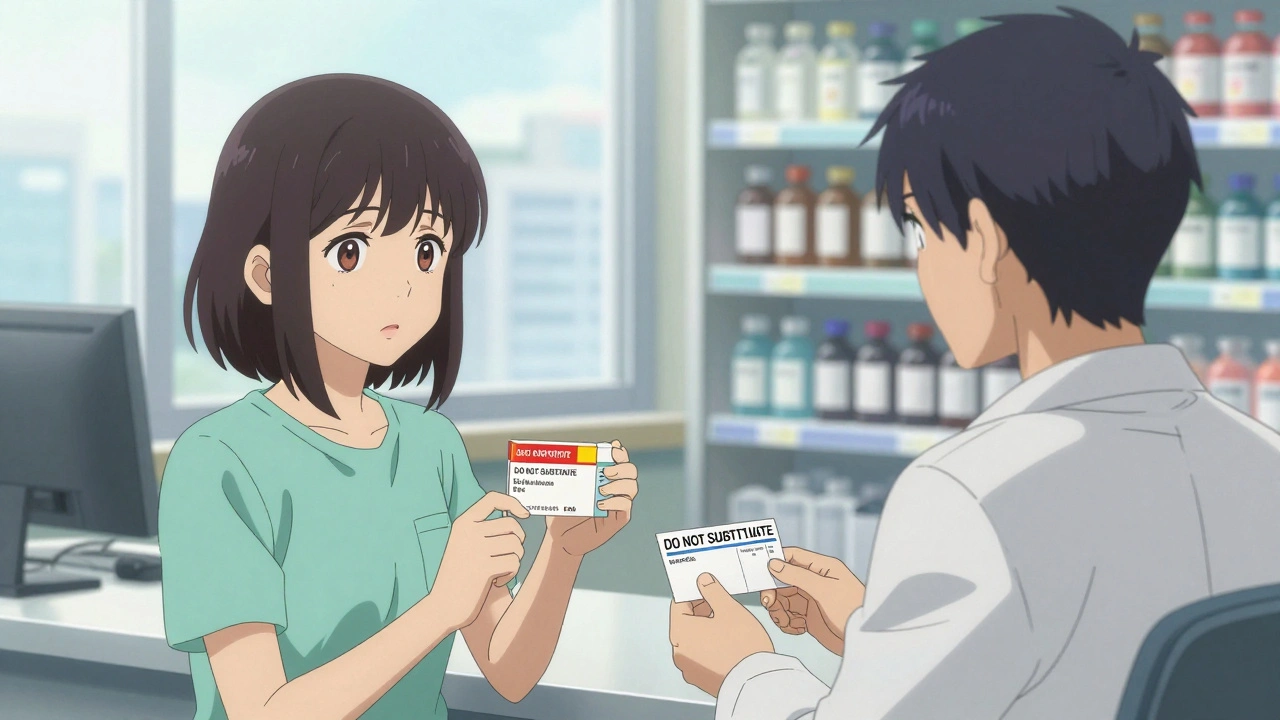
Every year, millions of Americans pick up prescriptions at the pharmacy, expecting to get the cheapest option available. But sometimes, the pharmacist hands you a brand-name drug - and it costs three times as much. That’s not a mistake. It’s because the doctor wrote do not substitute on the prescription.
What Does 'Do Not Substitute' Actually Mean?
When a doctor writes "do not substitute" or "DAW" (Dispense as Written) on a prescription, they’re telling the pharmacist: Don’t swap this brand-name drug for a generic version, no matter what. It’s a legal instruction, not a suggestion. In 49 states, pharmacists are required by law to follow it. The only exception? If the patient insists on the cheaper generic and signs a waiver - but even then, the pharmacist must still confirm the doctor’s intent. This isn’t about brand loyalty. It’s about safety. Some drugs don’t play nice when swapped out. Even tiny differences in how a generic is made can throw off how the body absorbs it. For certain conditions, that’s not just inconvenient - it’s dangerous.When Is a Brand Drug Really Necessary?
Not every prescription needs a brand-name drug. In fact, over 90% of prescriptions filled in the U.S. are generics - and they work just fine for most people. But there are specific cases where switching can cause real problems. Narrow therapeutic index (NTID) drugs are the biggest reason doctors write "do not substitute." These are medications where the difference between a safe dose and a toxic one is razor-thin. Examples include:- Warfarin (blood thinner)
- Levothyroxine (thyroid hormone)
- Phenytoin (seizure medication)
Why Don’t All Doctors Just Use Generics?
The truth? Many do. But some don’t - and not always for medical reasons. The American Medical Association says 8-12% of all prescriptions in 2022 had a "do not substitute" note. That sounds reasonable - until you look at the numbers by drug class. For biologics (like insulin or rheumatoid arthritis drugs), over 65% of prescriptions carry this note. For regular pills like antibiotics or blood pressure meds? Only 10%. That’s not because biologics are inherently riskier - it’s because they’re expensive, and biosimilars (the generic version of biologics) are still rare. Only 12 have been approved as "interchangeable" by the FDA as of late 2023. Some doctors admit they write "do not substitute" out of habit, not science. Harvard’s Dr. Aaron Kesselheim found that in some clinics, up to 30% of DNS requests were for drugs where generics have been proven safe for years. He blames pharmaceutical marketing: "Doctors get reps in their offices, get free samples, and sometimes don’t realize how much cheaper - and just as safe - the generic is." Meanwhile, the American College of Physicians warns that unnecessary DNS prescriptions cost the system $15.7 billion a year. That’s money that could go to patient care, not corporate profits.How Do You Know If You’re Getting a Brand Drug for the Right Reason?
If you’re handed a brand-name prescription and the price shocks you, don’t just pay it. Ask questions.- "Why is this brand only? Is there a safety reason?"
- "Has this happened before with generics?"
- "Can we try the generic with close monitoring?"
What Happens When the System Fails?
The process isn’t perfect. Pharmacists report that insurance systems reject "do not substitute" requests 15-20% of the time - even when the prescription is properly written. That means you might wait 20 minutes at the counter while the pharmacist calls the doctor’s office for clarification. Electronic health records make it worse. Many systems default to "allow substitution" unless the doctor manually overrides it. A 2022 report from Epic Systems found 32% of DNS orders had to be fixed by hand because the software didn’t recognize the doctor’s note. And in some states, the rules are messy. New York requires the exact phrase "Dispense as Written" with the doctor’s initials. California lets doctors click a box on an e-prescription. If a doctor in New York writes "do not substitute" without initials, the pharmacy might legally fill the generic anyway.







Shannara Jenkins
December 3, 2025 AT 05:09My grandma takes levothyroxine and switched generics last year-she got dizzy, her heart raced, and she almost passed out at the grocery store. We called the doctor, and they switched her back. Turns out, her body just doesn’t like the new filler. Never thought I’d say this, but sometimes the brand really is worth it.
Doctors aren’t just being greedy. Sometimes they’ve seen the fallout firsthand.
Arun kumar
December 3, 2025 AT 11:27bro i was in delhi last year and got my blood thinner from a local chemist, they gave me some indian generic, i felt like a ghost for 3 days. then i found out the active ingrediant was same but the coating was like chalk. my doc here in usa said same thing-ntid drugs? dont mess. india has diff standards, usa too sometimes. but the system? broken.
Zed theMartian
December 5, 2025 AT 09:53Oh please. Let me guess-you’re one of those people who thinks ‘brand’ means ‘better’ because you saw a commercial with a dog in a lab coat? The FDA’s bioequivalence standards are stricter than your ex’s text replies. 90-112% absorption? That’s not a loophole-it’s science.
Meanwhile, the real villain is Big Pharma’s $12 billion lobbying budget. Your ‘safety’ is just a marketing slogan with a stethoscope.
And no, your doctor didn’t ‘see the fallout.’ They got a free lunch from the rep who handed them a $200 pen.
Ella van Rij
December 5, 2025 AT 19:46So… you’re telling me the system’s designed to save money… unless you’re on insulin, then suddenly we’re in a medical thriller? 🙄
Also, my doctor wrote ‘do not substitute’ on my metformin. I asked why. He said ‘because I always have.’
And now I’m paying $180 a month for a pill that costs $4 in Mexico. Thanks, capitalism.
Also, typo: ‘dosage’ was spelled ‘doseage.’ I’m not even mad. Just… tired.
ATUL BHARDWAJ
December 6, 2025 AT 08:15India generics work fine for most. But for warfarin? We use brand. Because blood is serious. No joke.
Doctors here also write DAW not for profit but because patient died once on generic. Memory lasts longer than savings.
Cost matters. Life matters more.
Rebecca M.
December 6, 2025 AT 22:03Oh my god I just realized my insurance denied my brand-name asthma inhaler and I cried in the parking lot.
Not because I’m dramatic-because I have a 5-year-old who has asthma and the generic made her wheeze like a broken accordion.
So now I’m writing a Yelp review titled: ‘How My Kid Almost Died Because of a Pharmacy Algorithm.’
And yes, I’m tagging my senator.
Paul Keller
December 7, 2025 AT 09:10Let’s not romanticize the brand-name drug. The science is clear: for the vast majority of medications, generics are functionally identical. The FDA’s approval process is among the most rigorous in the world. The real issue isn’t pharmacological equivalence-it’s systemic inertia and corporate capture.
Doctors who default to ‘do not substitute’ without evidence are not practicing medicine-they’re abdicating their duty to educate. And pharmacies? They’re trapped in a broken reimbursement model that punishes efficiency.
The solution isn’t to ban generics-it’s to audit prescribing patterns, mandate patient education, and incentivize transparency. This isn’t about trust in drugs-it’s about trust in institutions. And right now, that trust is crumbling under the weight of profit-driven negligence.
Let’s fix the system, not just the script.
Elizabeth Grace
December 9, 2025 AT 01:49I got prescribed a brand-name seizure med after my last hospital stay. The pharmacist handed me the generic and I said ‘no, my doctor said no.’ He looked at me like I was insane. Then he said, ‘Ma’am, it’s the same chemical.’
I said, ‘Yeah, but my brain isn’t the same chemical.’
And then I cried. Not because I’m emotional-because I’ve had 3 seizures in 2 months and I’m not risking a fourth because someone thinks ‘80-125% absorption’ is good enough.
My body is not a lab experiment. And I’m not a cost center.