Banding in Medication: What It Means for Your Treatment and Safety
When you hear banding, the practice of grouping medications by risk, use, or regulatory status to guide safe prescribing. Also known as drug classification, it’s not just paperwork—it’s a real-world system that decides which drugs your doctor can prescribe easily, which need extra checks, and which could be dangerous if mixed. Think of it like sorting tools: you don’t hand a chainsaw to someone who’s never used a hammer. Same with meds. Banding helps pharmacists and doctors spot high-risk combinations before they cause harm.
This system shows up everywhere. In opioid prescribing, a category of drugs tightly controlled due to addiction and overdose risks. Also known as controlled substances, they’re often in the highest band because mixing them with antiemetics like ondansetron can trigger heart problems. That’s why posts like the one on opioid nausea and antiemetics matter—they’re not just about side effects, they’re about banding rules in action. Same with bisphosphonates, bone drugs linked to rare but severe jaw damage. Also known as MRONJ-risk medications, they’re flagged in banding systems because skipping dental care while on them is a silent danger. Even something as simple as taking your blood pressure pill with food or on an empty stomach ties into banding: some drugs are grouped by how sensitive they are to absorption changes, and getting it wrong can mean your treatment fails.
Bandings also explain why you might be switched from brand to generic, or why your doctor asks about every supplement you take. The system doesn’t just track danger—it tracks reliability. A drug like clozapine, an antipsychotic with life-saving power but serious blood monitoring needs. Also known as high-risk antipsychotic, it’s in the tightest band because one wrong dose can kill. That’s why posts on antipsychotic alternatives don’t just compare side effects—they’re comparing banding levels. When a drug gets recalled or has a safety alert—like recent updates on ADHD or Alzheimer’s meds—it’s often because the banding system flagged a pattern too late. And when e-prescribing systems cause transcription errors, it’s usually because the banding codes got lost in translation between programs.
What you’ll find below isn’t just a list of articles. It’s a map of how banding shapes your health—from how your insulin is stored during a shortage, to why secnidazole is considered safe in pregnancy while other antibiotics aren’t, to why your potassium levels matter when you’re on irbesartan/HCTZ. These aren’t random topics. They’re all connected by the invisible rules that tell doctors and pharmacists: this drug is high-risk, this combo is dangerous, this timing is critical. You don’t need to memorize the bands. But knowing they exist—and how they protect you—can help you ask the right questions before you take your next pill.
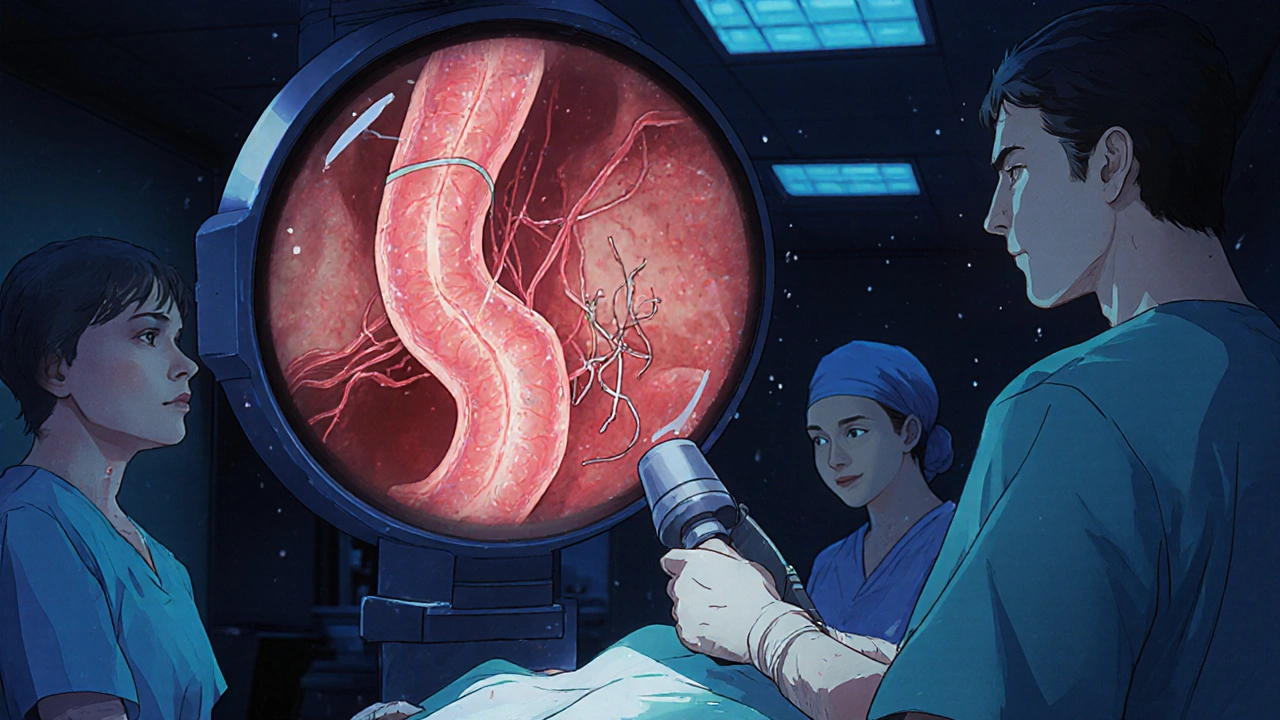
Variceal bleeding is a life-threatening complication of liver cirrhosis. Learn how endoscopic banding, beta-blockers like carvedilol, and prevention strategies can stop bleeding and save lives.
Recent-posts
Dec, 4 2025
Categories
Tags
- online pharmacy
- side effects
- drug interactions
- generic drugs
- online pharmacy UK
- drug safety
- opioid side effects
- pill organizer
- Tadalafil
- arthritis medication
- buy medication online
- prescription medication
- quit smoking
- motion sickness
- Sildenafil
- Vardenafil
- ED medication alternatives
- biologics
- medication safety
- generic medication prices