The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) doesn’t stop monitoring drugs once they’re on the market. In fact, some of the most important safety updates come after millions of people have been using a medicine for years. That’s because clinical trials-while thorough-can’t catch every possible side effect. Sometimes, rare reactions only show up when a drug is used by hundreds of thousands, or even millions, of patients over time. In 2025 alone, the FDA has issued at least eight major Drug Safety Communications (DSCs), each with real-world consequences for patients and providers.
What Are Drug Safety Communications?
Drug Safety Communications are official notices from the FDA that warn doctors and patients about newly discovered risks tied to approved medications. These aren’t recalls. They’re alerts. They tell you: "This medicine might be riskier than we thought. Here’s what to watch for." They’re required by law under Section 505(o)(3) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Every DSC must include: the specific safety concern, what evidence the FDA reviewed, what patients and doctors should do, and whether the drug’s label needs updating. The FDA pulls data from multiple sources: hospital reports, patient registries, clinical studies, and even social media trends flagged by its Sentinel Initiative-a system that tracks health records from 300 million Americans across 25 major healthcare networks.Opioid Labeling Changes: A Landmark Update
The biggest safety alert of 2025 came on July 31. The FDA mandated class-wide changes to the prescribing labels of all 46 opioid pain medications in the U.S. This isn’t just about one drug. It’s about every extended-release and long-acting opioid-oxycodone, morphine, hydromorphone, and others. The new labels now include hard numbers:- 1 in 12 patients (8.3%) who take opioids for more than 90 days will develop opioid use disorder.
- Long-term use increases the risk of fatal overdose by 3.5 times compared to short-term use.
- Drug interactions with gabapentinoids (like Neurontin and Lyrica) can cause dangerous breathing suppression.
- A rare but deadly brain condition called toxic leukoencephalopathy has been linked to opioid overdose, even in people who didn’t take other drugs.
Other Major Safety Alerts in 2025
Not all DSCs affect every patient. Some are narrow but critical:- May 16, 2025: Zyrtec and Xyzal (cetirizine and levocetirizine) now carry a warning about drowsiness and impaired driving. The FDA reviewed over 1,200 reports of accidents linked to these allergy meds, especially in older adults and those taking other sedatives.
- June 30, 2025: Extended-release ADHD stimulants (like Adderall XR and Concerta) now require weight monitoring in children under 6. These drugs can suppress appetite so severely that kids lose 10% or more of their body weight in months. The FDA recommends checking weight every 3 months.
- June 25, 2025: Pfizer’s Comirnaty and Moderna’s Spikevax got updated warnings about myocarditis. In males aged 12-29, there are now 1,195 confirmed cases per million second doses. Most cases are mild and resolve quickly, but the FDA now advises spacing doses further apart for this group.
- August 27, 2025: Clozapine, an antipsychotic used for treatment-resistant schizophrenia, had its Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) removed. This rare move means the FDA now considers the drug safer than previously thought-thanks to better blood monitoring and reduced infection risks.
- August 28, 2025: Leqembi, a new Alzheimer’s drug, now requires two MRIs-at 5 and 14 months after starting treatment. The FDA found 274 cases of brain swelling or bleeding (called ARIA) in the first year of use. Early detection saves lives.
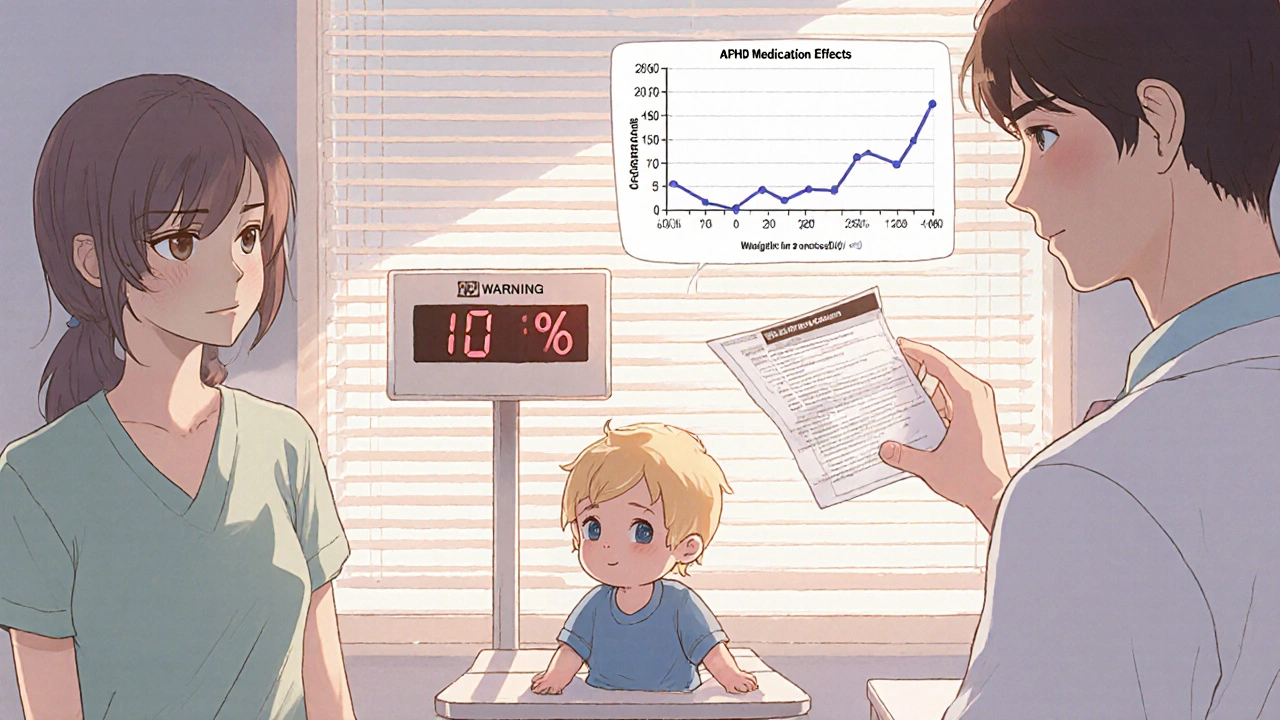
What Should You Do as a Patient?
If you’re taking any of these medications, don’t panic. But do take action:- Check your prescription. Is it on the list? Look up the generic or brand name on the FDA’s Drug Safety Communications page.
- Don’t stop cold turkey. Abruptly stopping opioids, ADHD meds, or antipsychotics can be dangerous. Talk to your doctor first.
- Ask about monitoring. For opioids, ask: "Should I be checked every 3 months?" For ADHD meds in kids: "Should we check weight again?" For Leqembi: "When’s my next MRI?"
- Know the red flags. For opioids: confusion, slow breathing, extreme drowsiness. For stimulants: weight loss over 5% in 3 months. For vaccines: chest pain, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat after vaccination.
What Should Doctors and Pharmacies Do?
Healthcare providers are on the front lines. The FDA expects them to:- Re-evaluate opioid therapy every 1-4 weeks at the start, then every 3 months for stable patients.
- Measure weight in young children on stimulants before starting and every 90 days.
- Screen for drug interactions-especially gabapentinoids and benzodiazepines with opioids.
- Advise patients on heat risks with Transderm Scōp (patch for motion sickness). Avoid hot tubs, saunas, and direct sun if you’re wearing it.
- Keep copies of updated prescribing information on hand. The FDA doesn’t send out paper updates. You have to download them.
Why Is This Happening Now?
The opioid crisis didn’t vanish. It evolved. The FDA is now using real-world data to fix gaps left by old clinical trials. The pharmaceutical industry is spending more on post-approval safety studies than ever before-up 28.5% from 2020 to 2024. The Opioid Postmarketing Consortium alone spent $187 million to get those new numbers on labels. Biologics are another big driver. Drugs like Leqembi, CAR-T therapies, and mRNA vaccines are complex. Their risks don’t always show up in small trials. That’s why the FDA’s Sentinel Initiative is expanding. By 2027, it’s expected to detect 2-3 times more safety signals than it does now. The FDA’s 2026-2030 plan says it wants to issue safety alerts within 30 days of confirming a risk. Right now, it takes 60-90 days. That’s changing. Faster alerts mean faster changes.What’s Next?
The FDA is now drafting rules that could require all drugs with black box warnings-the strongest safety alert-to generate real-world evidence within two years of approval. That means companies might have to pay for large, long-term studies even before they make a profit. That could slow down drug development. Or it could make drugs safer. Either way, the goal is clear: patients shouldn’t have to be the ones discovering side effects.Frequently Asked Questions
Are all medication recalls due to safety issues?
No. Most recalls happen because of manufacturing problems-like contamination, incorrect dosing, or broken packaging-not because the drug is dangerous. Safety-related recalls are rarer and usually tied to serious side effects like organ damage, overdose risk, or allergic reactions. The FDA separates these into two categories: safety alerts (Drug Safety Communications) and recalls (which involve removing products from shelves).
Can I still take my opioid if I’ve been on it for years without problems?
Maybe, but you need to talk to your doctor. The new FDA warning says long-term use carries a 1 in 12 risk of developing opioid use disorder-even if you’ve never misused it. That doesn’t mean you have to stop. But it does mean you should review your treatment plan. Are there non-opioid options? Is your pain still under control? Is your dose the lowest effective one? Your doctor should reassess this every 3 months.
What should I do if I think a medication is causing a side effect?
Report it. The FDA’s Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) and MedWatch program let patients and doctors report suspected side effects. Even if you’re not sure, report it. The FDA uses these reports to spot patterns. One report might not mean much, but 50 similar reports? That’s a signal. You can file a report online at fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Do these safety updates mean the drugs are unsafe?
Not necessarily. They mean the risks are better understood now. All medicines have risks and benefits. For many patients, opioids still provide essential pain relief. Leqembi slows Alzheimer’s progression. ADHD meds help kids focus. The goal isn’t to ban these drugs-it’s to make sure they’re used safely, with full awareness of the risks. The FDA’s job is to balance access with safety.
How often does the FDA issue these safety alerts?
The number has been rising. In 2020, the FDA issued 47 Drug Safety Communications. In 2024, that number jumped to 68. That’s a 44.7% increase in just four years. The trend is continuing in 2025, with at least eight major alerts already issued by August. This reflects better data collection, more complex drugs, and a stronger focus on long-term safety.
Where can I find the latest FDA drug safety updates?
Go directly to the FDA’s official Drug Safety Communications page: fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/drug-safety-communications. Bookmark it. The site is updated daily. You can search by drug name, date, or condition. It’s the only place with official, verified information-not news sites, not social media.









Scarlett Walker
November 15, 2025 AT 07:35Hey, just wanted to say this is actually really helpful info. I’ve been on oxycodone for three years and had no idea the risk was 1 in 12. My doctor never mentioned it. I’m scheduling a check-up this week to talk about alternatives. Thanks for breaking it down so clearly!
Anjan Patel
November 15, 2025 AT 16:21Oh, so now the FDA is playing God again? They didn’t even wait for a proper study to come out before slapping warnings on everything. People are dying from opioid withdrawal because they panic and quit cold turkey thanks to these fear-mongering alerts. This isn’t safety-it’s control. And don’t get me started on the vaccine myocarditis numbers-they’re basically zero for all practical purposes. Why are we treating healthy teens like walking time bombs?
Hrudananda Rath
November 16, 2025 AT 19:05One must observe, with profound intellectual consternation, the sheer epistemological fragility of contemporary regulatory science. The FDA, in its infantile reliance upon post hoc surveillance data-largely drawn from unvalidated, algorithmically flagged social media reports and fragmented electronic health records-has abandoned the rigorous epistemic standards that once defined pharmacovigilance. The 1 in 12 statistic? A statistical artifact, likely inflated by selection bias and confounding variables. Where is the randomized controlled trial? Where is the double-blind placebo control? One is left to wonder whether the agency has been captured by activist NGOs masquerading as public health advocates.
Brian Bell
November 17, 2025 AT 22:12Bro this is wild. I didn’t even know Zyrtec could make you crash while driving 😳 My grandma’s on it and she drives to the store every day. Gonna send her this link. Also, Leqembi MRIs? That’s a lot of $$$-but if it saves your brain, worth it imo. 🤞
Nathan Hsu
November 18, 2025 AT 13:52Let me just say, this is the most comprehensive, meticulously documented, and desperately needed public health update I’ve seen in years-yes, years! The FDA has, against all odds, risen to the occasion with an unprecedented level of transparency, diligence, and scientific integrity. The inclusion of exact percentages, the acknowledgment of real-world data, the emphasis on patient autonomy and physician responsibility-it’s a masterclass in responsible governance. I am, frankly, moved. And yes, I will be sharing this with my entire extended family in Mumbai, Delhi, and Bangalore. We need more of this. More. More. More.
Ashley Durance
November 19, 2025 AT 02:00The 1 in 12 opioid use disorder statistic is misleading. It conflates dependence with addiction. Dependence is physiological; addiction is behavioral. Most patients on long-term opioids are not addicted-they’re managing chronic pain. The FDA’s wording intentionally stigmatizes. And the myocarditis numbers? 1,195 per million sounds scary until you realize that’s 0.12%. Meanwhile, COVID-related myocarditis is 10x higher. They’re cherry-picking data to push a narrative. The real issue? Doctors aren’t trained to differentiate between these terms. The FDA should fix that-not scare people off meds.
Scott Saleska
November 20, 2025 AT 22:17Hey, I just wanted to say-I’m a nurse in Ohio, and we’ve been seeing this exact thing with ADHD meds in kids. One 5-year-old lost 15% of his body weight in 4 months. We caught it because his mom brought him in for a cold, but his shirt was hanging off him. The FDA’s weight check recommendation? Long overdue. But here’s the thing-most pediatricians don’t even have scales that go below 30 lbs. We’re using baby scales and writing notes by hand. The system’s broken. I hope this pushes for better tools.
Ryan Anderson
November 22, 2025 AT 05:46This is exactly the kind of transparency we need. 🙌 The FDA isn’t perfect, but they’re trying. Real-world data > small trials. Period. I’m glad they’re pushing for mandatory post-market studies. If a drug costs $500k a year (looking at you, Leqembi), the company should pay for the long-term safety data. Also, props for the clear red flags list. Saved this for my mom-she’s on gabapentin and opioids. She’s gonna call her doc tomorrow. 💪
Eleanora Keene
November 24, 2025 AT 02:32Okay I just read this and I’m so proud of how far we’ve come. I used to be terrified of my antidepressants, but now I know how to ask the right questions. I’m going to print this out and take it to my next appointment. And if you’re a doctor reading this-you’re doing important work. Don’t give up. We see you. 💛
Joe Goodrow
November 25, 2025 AT 19:05Why is the FDA listening to some foreign study funded by Big Pharma? We don’t need their fear tactics. Opioids saved my brother’s life after his back surgery. Now they want to ban them because some junkie got addicted? That’s not safety-that’s socialism. And why are we giving out MRIs for a drug made by a company that’s not even American? We need American-made meds, American data, American oversight. Not this globalist nonsense.
Don Ablett
November 26, 2025 AT 15:41The Sentinel Initiative’s expansion to 300 million records represents a paradigm shift in pharmacovigilance methodology. However, the absence of a standardized data dictionary across participating institutions introduces significant heterogeneity in outcome ascertainment. Without harmonized coding protocols-such as SNOMED CT or LOINC-the validity of signal detection remains questionable. Furthermore, the assumption that social media trends constitute valid epidemiological data lacks theoretical grounding in classical biostatistics. The FDA should prioritize methodological rigor over speed.